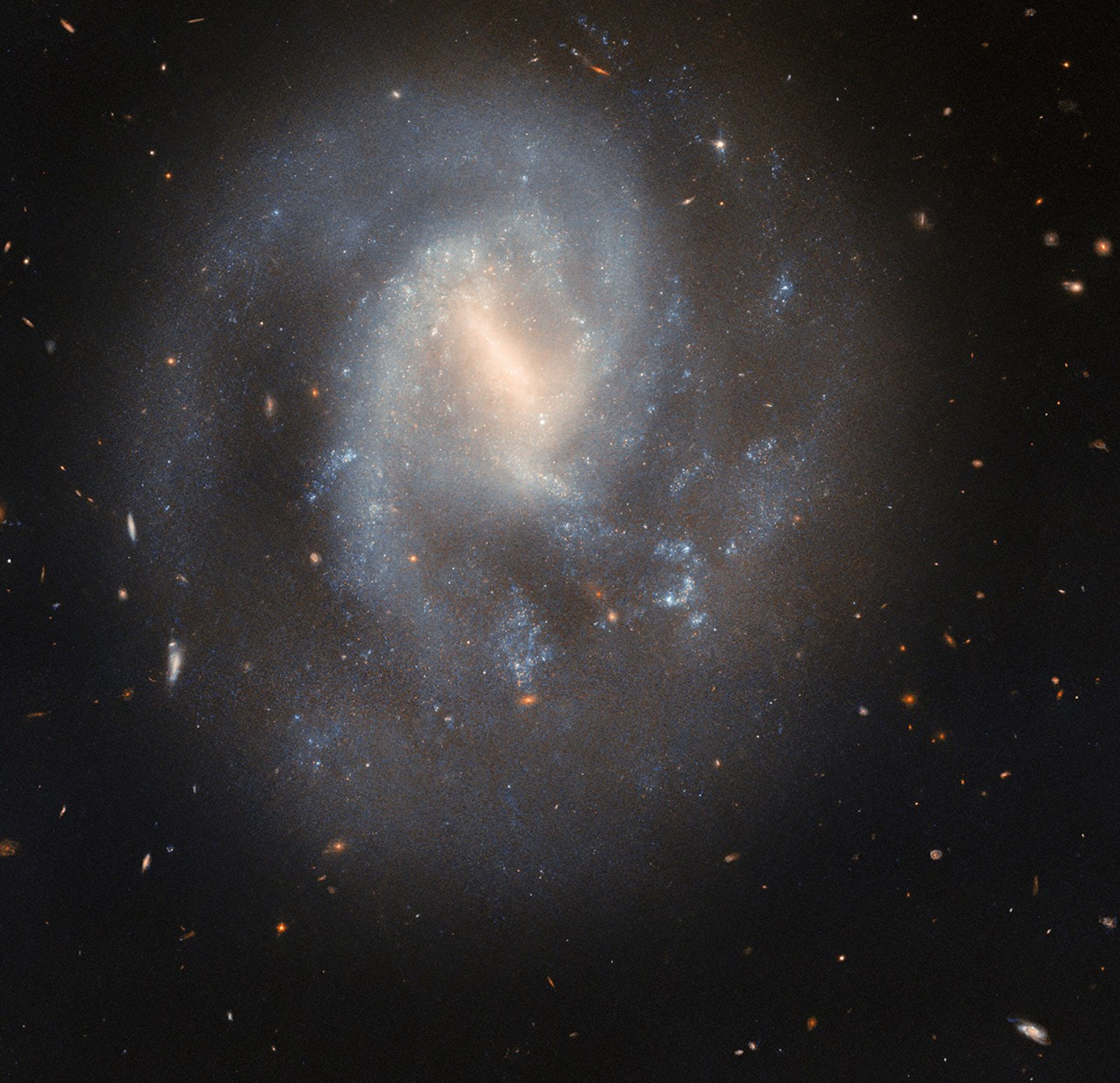
This serene spiral galaxy hides a cataclysmic past. The galaxy IC 758, shown in this NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope image, is situated 60 million light-years away in the constellation Ursa Major. Hubble captured this image in 2023. IC 758 appears peaceful, with its soft blue spiral arms curving gently around its hazy barred center. However, […]...
2 min read
Hubble Studies a Spiral’s Supernova Scene
This serene spiral galaxy hides a cataclysmic past. The galaxy IC 758, shown in this NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope image, is situated 60 million light-years away in the constellation Ursa Major.
Hubble captured this image in 2023. IC 758 appears peaceful, with its soft blue spiral arms curving gently around its hazy barred center. However, in 1999, astronomers spotted a powerful explosion in this galaxy. The supernova SN 1999bg marked the dramatic end of a star far more massive than the Sun.
Researchers do not know exactly how massive this star was before it exploded, but will use these Hubble observations to measure the masses of stars in SN 1999bg’s neighborhood. These measurements will help them estimate the mass of the star that went supernova. The Hubble data may also reveal whether SN 1999bg’s progenitor star had a companion, which would provide additional clues about the star’s life and death.
A supernova represents more than just the demise of a single star — it’s also a powerful force that can shape its neighborhood. When a massive star collapses, triggering a supernova, its outer layers rebound off its shrunken core. The explosion stirs the interstellar soup of gas and dust out of which new stars form. This interstellar shakeup can scatter and heat nearby gas clouds, preventing new stars from forming, or it can compress them, creating a burst of new star formation. The cast-off layers enrich the interstellar medium, from which new stars form, with heavy elements manufactured in the core of the supernova.
Text Credit: ESA/Hubble
Media Contact:
Claire Andreoli (claire.andreoli@nasa.gov)
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, MD